我的博文
肌纤维瘤和肌纤维瘤病
概述
肌纤维瘤/肌纤维瘤病(myofibroma/myofibromatosis)最初由Williams和Schrum于1951年首先报道,起初命名为先天性纤维
肉瘤。1954年Stout将其更名为幼年性纤维瘤病(juvenile fibromatosis)或先天性系统性纤维瘤病(congenital
generalized fibromatosis)。1981年Chung和Enzinger的报道显示,该肿瘤属于肌纤维母细胞性病变,故又将其重新命名为
婴儿肌纤维瘤病(infantile myofibromatosis)。因肿瘤偶可发生于成人,故在2002版WHO分类中,去掉了“婴儿”这一前
缀。在形态学上,肌纤维瘤/肌纤维瘤病与肌周皮细胞瘤以及所谓的婴幼儿型血管外皮瘤有延续,故在2013版WHO分类中将其
划归肌周皮细胞瘤名下。
临床表现
多发生于婴儿,偶可见于成人。临床上有三种类型:
①孤立性(肌纤维瘤):好发于皮肤,可延伸至皮下、肌肉和骨。最常见部位头颈部、躯干和四肢;
②多中心性(肌纤维瘤病):不常见,包括两种亚型:一个是软组织/骨的多发性病灶不伴内脏累及;另一个是伴有内脏
(肺、心脏、胃肠等)累及;
③成年型:多表现为肢体和头颈部皮肤或口腔内缓慢生长的无痛性肿块。
大体形态
无包膜,直径多数为1cm左右;质地坚实,瘢痕样,切面灰白。
组织形态学
孤立性和多中心性的镜下形态相似,呈结节状或多结节状生长,并具有明显的区带现象:由淡染的周边区和深染的中央区组
成;20%病例可见瘤细胞突向血管腔内生长。
周边区由结节状或短束状排列的胖梭形细胞组成,胞质嗜伊红,形态上介于纤维母细胞和平滑肌细胞之间(肌纤维母细
胞);
中央区由圆形或小多边形的原始间叶细胞组成,呈实性片状分布,或围绕分支状的血管呈血管外皮瘤样排列,可见核分裂象
和坏死,后者常伴钙化。
间质:黏液样,胶原化或玻璃样变性,可有灶性出血和囊性变。
成人肌纤维瘤主要发生于皮下呈结节状,主要由嗜伊红的肌纤维母细胞组成,结节周边可见少量相对较为原始的间叶细胞,
可有血管外皮瘤样结构。
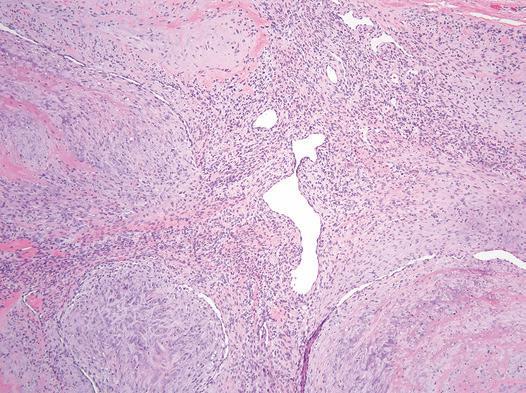
Figure Myofibroma. The tumor shows a biphasic appearance: a highly cellular component with prominent thin-
walled blood vessels is surrounded by nodular, fascicular areas.
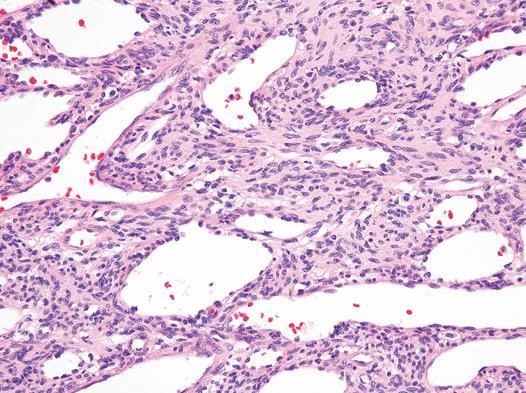
Figure Myofibroma. The tumor cells in the central area are small and ovoid with a primitive appearance.
Note the prominent branching thin-walled blood vessels.
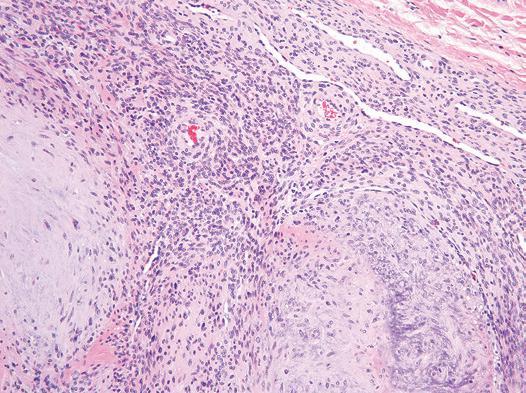
Figure Myofibroma. A basophilic, pseudochondroid appearance of the myoid nodules is typical.
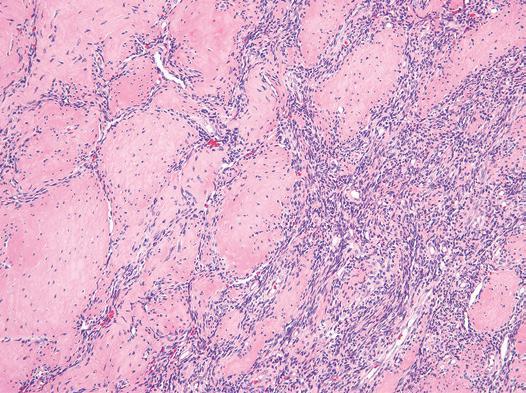
Figure Myofibroma. In some myofibromas the myoid nodules show a hyalinized appearance.
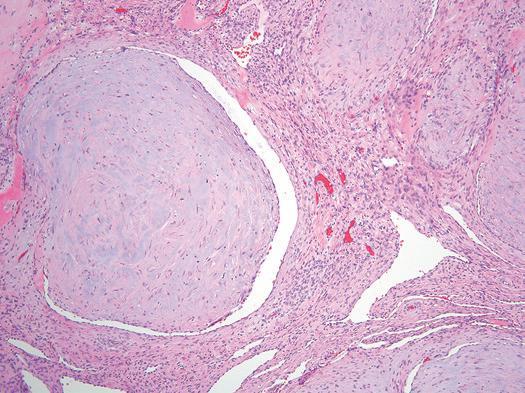
Figure Myofibroma. Myoid nodules often protrude into the lumina of thin-walled blood vessels (“telescoping”).
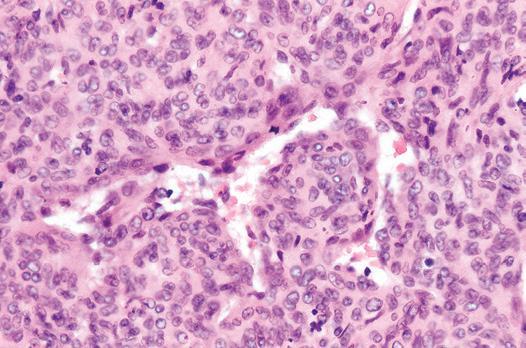
Figure Infantile Myofibroma. Primitive round and polygonal cells with irregular branching blood vessels form hemangiopericytoma-like areas.
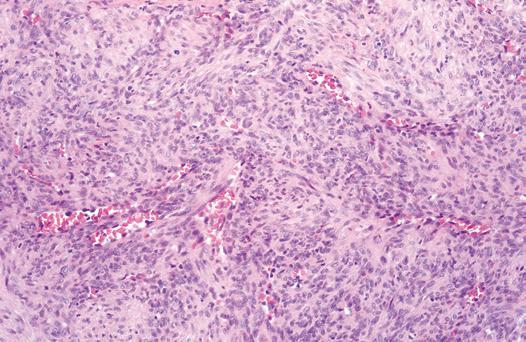
Figure Infantile Myofibroma. Spindle cell nodules merge with hemangiopericytoma-like foci.
免疫组化
肌纤维母细胞性成分和原始间叶细胞成分均可以表达Vimentin和a-SMA,肌纤维母细胞性成分还可表达MSA,不表达desmin和
S100,以及EMA和CK。
The endothelial cells in the hemangiopericytoma-like areas are reactive for CD34.
分子遗传学
Mutations in PDGFRB, NDRG4, and NOTCH3 have been identified.
Antonescu et al. showed that subsets of highly cellular myofibromas contain SRF-RELA fusions; these cases do
not appear to have also been analyzed for PDGFRB mutations. The relationship of the cases described by
Haller et al. as pediatric and adult “soft tissue sarcomas with NTRK1 gene fusions” to highly cellular
myofibromas is unclear.


鉴别诊断
①婴幼儿型血管外皮瘤:与肌纤维瘤病属于同一种病变的不同瘤谱,或者说是一种具有血管外皮瘤样结构的肌纤维瘤病;
②婴儿型纤维肉瘤:瘤细胞偏丰富,核分裂象多见。婴儿型纤维肉瘤具有t(12;15)(p13;q25)及其产生的ETV6-NTRK3R基
因融合;
③大龄儿童/成人病例还需与结节性筋膜炎进行鉴别;
④具有血管外皮瘤样结构的肿瘤:包括骨外尤文肉瘤/PNET、间叶性软骨肉瘤和滑膜肉瘤等;当肌纤维瘤病以呈血管外皮瘤样
排列的原始间叶细胞成分为主时,应与上述肿瘤进行鉴别;
治疗与预后
孤立性病变采用局部切除。累及内脏和全身广泛性病变者预后不佳。
参考文献
[1] 王坚,朱雄增. 软组织肿瘤病理学[M].2017.
[2] Hornick JL. Practical Soft Tissue Pathology: A Diagnostic Approach[M].2018.
[3] Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors[M]. 2020.
我要评论






共0条评论