我的博文
软组织小圆细胞肿瘤的病理诊断(一) 
各位老师,大家新年好!小圆细胞肿瘤的诊断虽然不是最难的,但在实际工作中偶尔也会让病理医生感到困惑,尤其是小活检标本或穿刺标本。今天有幸邀请到了66位经分子遗传学证实的尤文氏家族肿瘤。现在我把宝贵的时间交给这66位嘉宾,先请他们的代表来介绍一下大家的基本情况。

非常感谢Folpe(文章作者)邀请我们来和华夏病理网的老师一起来讨论小圆细胞肿瘤的病理诊断。我们今天到来的66位成员,中位年龄18岁(3~65岁);男性32位,女性31位,3位因资料不全未告知性别;他们分别来自骨和软组织。55位因具有典型的组织学表现,所以大家都很熟悉,其中46位是ES、9位是PNET;还有11位需要仔细辨认,详见下文图片。CD99和FLI-1在我们家族肿瘤中具有非常重要的诊断价值,几乎100%的肿瘤阳性,但千万不要看到CD99和FLI-1同时阳性的小圆细胞肿瘤就认为是我们家族成员。其他阳性指标有PanCK(18/56,32%)、34BE12(3/55,5%)、CD117(13/54,24%)、desmin(1/56,2%)。当形态学不典型时,基因检测对诊断有一定的帮助。问题又来了,很多肿瘤都存在EWSR1基因易位,因此还需结合形态学、免疫表型、临床资料等综合分析。
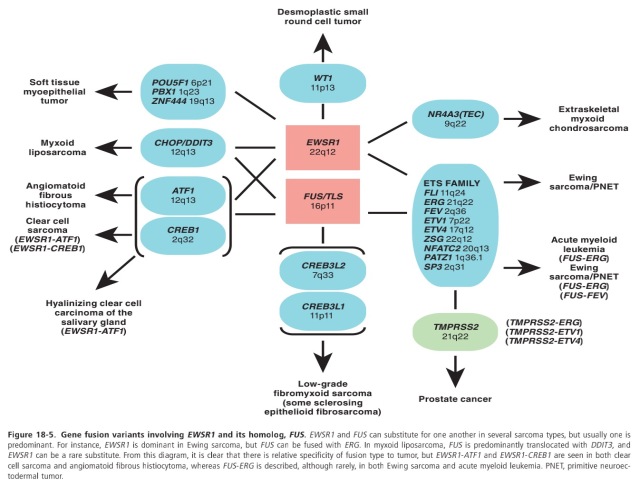
我们还是看图说话吧……
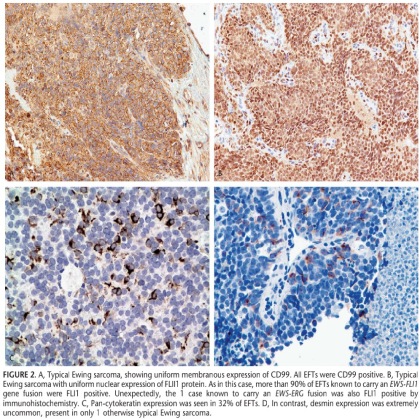
FIGURE 2. A, Typical Ewing sarcoma, showing uniform membranous expression of CD99. All EFTs were CD99 positive. B, Typical Ewing sarcoma with uniform nuclear expression of FLI1 protein. As in this case, more than 90% of EFTs known to carry an EWS-FLI1 gene fusion were FLI1 positive. Unexpectedly, the 1 case known to carry an EWS-ERG fusion was also FLI1 positive by immunohistochemistry. C, Pan-cytokeratin expression was seen in 32% of EFTs. D, In contrast, desmin expression was extremely uncommon, present in only 1 otherwise typical Ewing sarcoma.
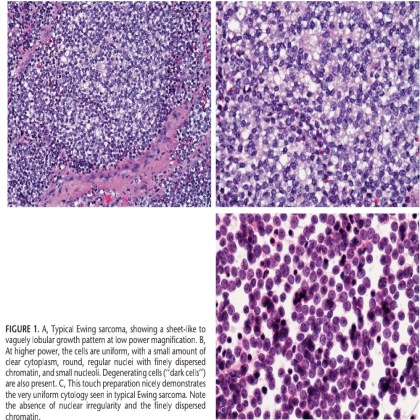
FIGURE 1. A, Typical Ewing sarcoma, showing a sheet-like to vaguely lobular growth pattern at low power magnification. B, At higher power, the cells are uniform, with a small amount of clear cytoplasm, round, regular nuclei with finely dispersed chromatin, and small nucleoli. Degenerating cells (‘‘dark cells’’) are also present. C, This touch preparation nicely demonstrates the very uniform cytology seen in typical Ewing sarcoma. Note the absence of nuclear irregularity and the finely dispersed chromatin.
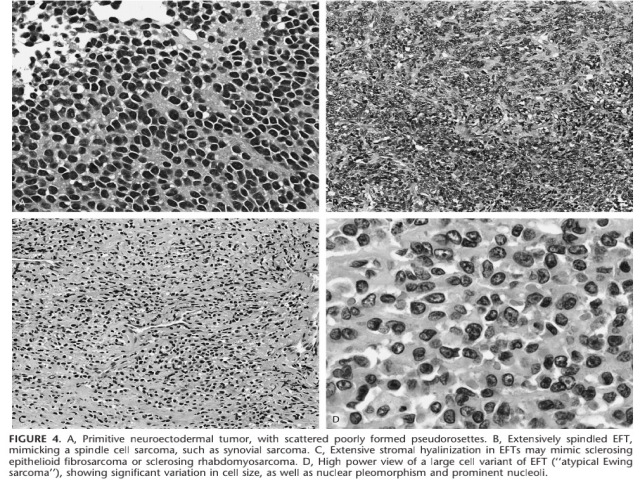
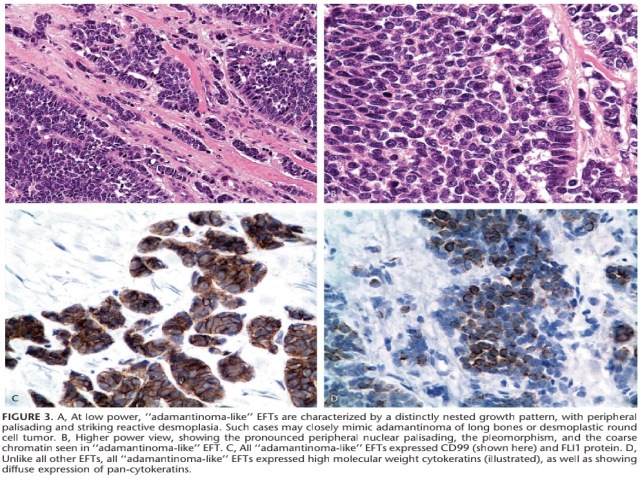
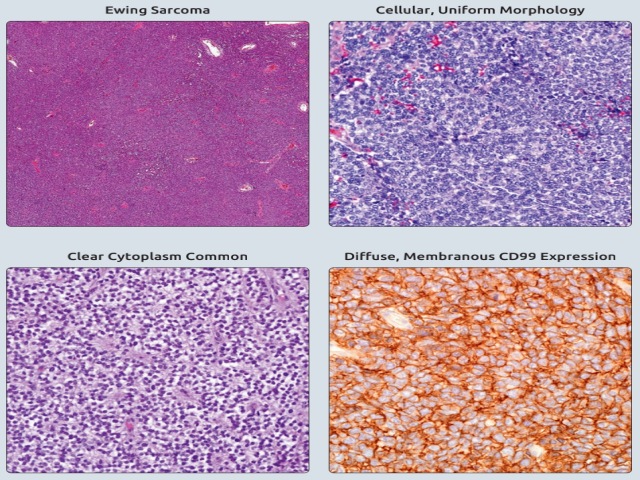
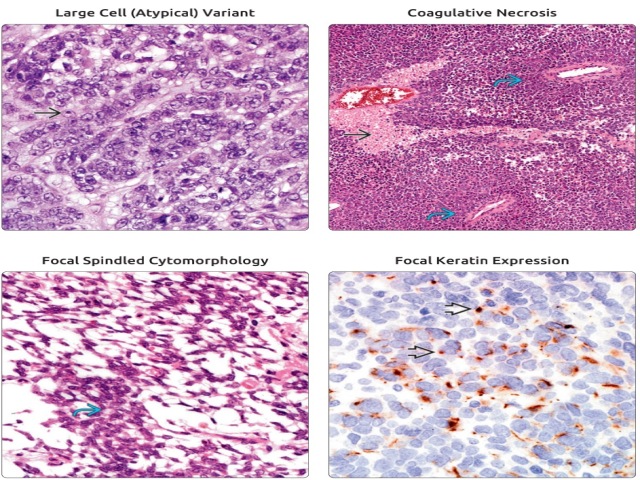
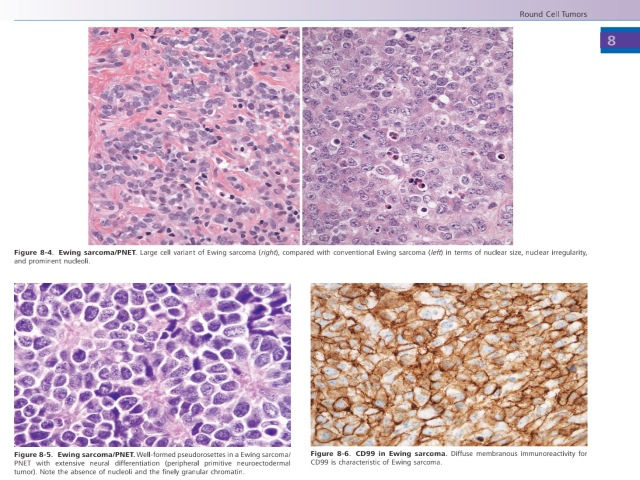
Figure 8-4. Ewing sarcoma/PNET. Large cell variant of Ewing sarcoma (right), compared with conventional Ewing sarcoma (left) in terms of nuclear size, nuclear irregularity, and prominent nucleoli.
Figure 8-5. Ewing sarcoma/PNET. Well-formed pseudorosettes in a Ewing sarcoma/PNET with extensive neural differentiation (peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor). Note the absence of nucleoli and the finely granular chromatin.
Figure 8-6. CD99 in Ewing sarcoma. Diffuse membranous immunoreactivity for CD99 is characteristic of Ewing sarcoma.
尤文氏肉瘤的典型形态学表现为:片状分布的原始幼稚小圆细胞由纤维结缔组织分隔呈分叶状,瘤细胞圆或卵圆形,胞质少,界限不清,有时胞质内含糖原呈空泡状,核膜明显,染色质粉尘状,可有1~2个不明显的小核仁,核分裂象数目不等,肿瘤性坏死多见,间质富于薄壁血管。部分病例出现Homer-Wright菊形团或围绕血管分布的假菊形团及乳头状结构;有时瘤细胞浸润于纤维结缔组织间,受到挤压,核深染,列兵状排列;有时肿瘤内出血明显,出现假血管腔隙或假腺泡结构;有时出现体积小、核深染、胞质少的“暗细胞”,与周围体积较大、染色质空泡状、胞质相对丰富的“亮细胞”混杂相间。
尤文氏肉瘤的其他形态学表现:一些肿瘤可表现为核增大、核形态不规则、核仁明显等不典型形态,梭形细胞、造釉细胞瘤样结构或间质明显硬化,易被误诊为滑膜肉瘤、促结缔组织增生性小圆细胞肿瘤、硬化型上皮样纤维肉瘤或硬化型横纹肌肉瘤。
参考文献:
[1]涉及EWSRl基因易位的软组织肿瘤[J].
[2]Morphologic and Immunophenotypic Diversity in Ewing Family Tumors:A Study of 66 Genetically Confirmed Cases[J].
[3]DIAGNOSTIC PATHOLOGY: SOFT TISSUE TUMORS[M].
[4]PRACTICAL SOFT TISSUE PATHOLOGY: A DIAGNOSTIC APPROACH[M].
我要评论






共0条评论