我的博文
母细胞性浆细胞样树突细胞肿瘤
Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm | 母细胞性浆细胞样树突细胞肿瘤 |
【Definition】 Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm (BPDCN) is a clinically aggressive tumour derived from the precursors of plasmacytoid dendritic cells (PDCs, also called professional type I interferon- producing cells or plasmacytoid monocytes), with a high frequency of cutaneous and bone marrow involvement and leukaemic dissemination. | 【定义】 母细胞性浆细胞样树突细胞肿瘤(BPDCN)是一种临床侵袭性肿瘤,来源于浆细胞样树突状细胞(PDCs,也称为专业的I型干扰素产生细胞或浆细胞样单核细胞)的前体,常有皮肤和骨髓受累和白血病播散。 |
【ICD-O code 】 9727/3 | 【ICD-0编码】 9727/3 |
【Synonyms】 Blastic NK-cell lymphoma (obsolete); agranular CD4+ NK leukaemia (obsolete); blastic NK leukaemia/lymphoma (obsolete); agranular CD4+ CD56+ haematodermic neoplasm/tumour | 【同义词】 母细胞性NK细胞淋巴瘤(过时); 无颗粒CD4+ NK白血病(过时); 母细胞性NK白血病/淋巴瘤(过时); 无颗粒CD4+CD56+血液皮肤肿瘤; |
【Epidemiology】 This rare form of haematological neoplasm has no known racial or ethnic predilection. The male-to-female ratio is 3.3:1. Most patients are elderly, with a mean/median patient age at diagnosis of 61-67 years, but this neoplasm can occur at any age, including in children. | 【流行病学】 这种罕见的血液肿瘤没有已知的种族或民族偏好。男女比例为3.3:1。大多数患者为老年人,诊断时的平均/中位患者年龄为61~67岁,但这种肿瘤可发生在任何年龄,包括儿童。 |
【Etiology】 There are currently no clues to the etiology of BPDCN, but its association with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) in some cases may suggest a related pathogenesis. There is no association with EBV. | 【病因学】 目前还未见关于BPDCN的发病机制线索,但在某些病例中,它与骨髓增生异常综合征(MDS)的联系可能暗示了相关的发病机理。与EBV无关。 |
【Localization】 The disease tends to involve multiple sites, most commonly the skin (involved in 64-100% of cases), followed by the bone marrow and peripheral blood (in 60-90%) and lymph node (in 40-50%). | 【部位】 这种疾病往往累及多个部位,最常见的是皮肤(64~100%的病例),其次是骨髓和外周血(60~90%)和淋巴结(40~50%)。 |
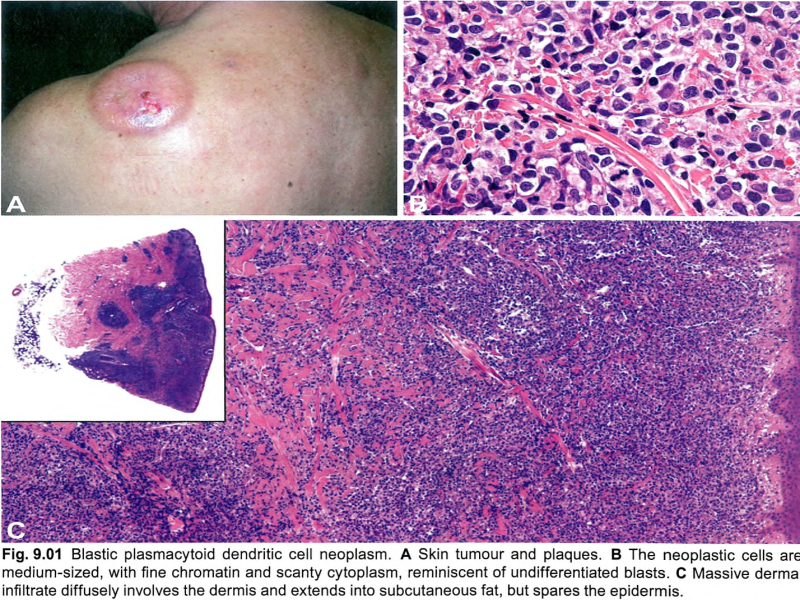
【Clinical features】 ①Skin manifestations are the most frequent clinical presentation of typical cases of BPDCN, and the diagnosis is made on skin biopsy. ② Patients usually present with asymptomatic solitary or multiple lesions. Three types of presentation are most commonly observed: an isolated (one or few) purplish nodule type (accounting for two thirds of cases), an isolated (one or few) bruise-like papule type, and a disseminated type with purplish nodules and/or papules and/or macules. ③ Isolated nodules are preferentially found on the head and lower limbs and can be > 10 cm in diameter. ④ The isolated bruise-like papule type is clinically very challenging. ⑤ The disseminated type is the most characteristic clinical presentation. ⑥ In some patients lacking skin involvement and with leukaemic presentation, the diagnosis is made based on peripheral blood or bone marrow analyses. ⑦ Regional lymphadenopathy at presentation is common (seen in 20% of cases). ⑧ Cytopenias (especially thrombocytopenia) can occur at diagnosis and in a minority of cases is severe, indicating bone marrow failure. ⑨ About 10-20% of cases of BPDCN are associated with or develop into other myeloid neoplasms, most commonly chronic myelomonocytic leukaemia, but also MDS or acute myeloid leukaemia (AML). ⑩ BPDCN must be distinguished from mature plasmacytoid dendritic cell proliferation (MPDCP), in which PDCs are morphologically mature and CD56-negative. This condition may be associated with cutaneous lesions (rash, macules or papules, and rarely nodules) together with lymph node and/or bone marrow infiltration. MPDCP is invariably associated with a myeloid disorder (most commonly chronic myelomonocytic leukaemia, MDS, or AML). | 【临床特征】 ① 皮肤表现是BPDCN典型病例最常见的临床表现,是通过皮肤活检诊断的。 ② 患者通常表现为无症状的单发或多发病灶。最常观察到三种类型的表现:孤立的(一个或几个)紫色结节型(占病例的三分之二)、孤立的(一个或几个)瘀伤样丘疹型和带有紫色结节和/或丘疹和/或斑疹的播散型。 ③ 孤立结节常出现在头部和下肢,直径可大于10cm。 ④ 孤立的瘀伤样丘疹类型在临床上非常具有挑战性。 ⑤ 播散型是最典型的临床表现。 ⑥ 在一些表现为白血病的无皮肤受累患者的诊断是基于外周血或骨髓分析。 ⑦ 表现为区域淋巴结肿大是常见的(20%的病例可见)。 ⑧ 血细胞减少症(尤其是血小板减少症)可在诊断时出现,少数病例严重,表明骨髓衰竭。 ⑨ 约10~20%的BPDCN与其他髓系肿瘤有关或发展为其他髓系肿瘤,最常见的是慢性粒单核细胞白血病,但也有MDS或急性髓系白血病。 ⑩ BPDCN必须与成熟浆细胞样树突状细胞增生区分开来,在成熟浆细胞样树突状细胞增生中,PDC在形态学上是成熟的且CD56阴性。这种情况可能与皮肤病变(皮疹、斑疹或丘疹,以及罕见的结节)以及淋巴结和/或骨髓浸润有关。MPDCP总是与髓系疾病(最常见的是慢性粒单核细胞白血病、MDS病或AML)相关。 |
【Microscopy】 ① BPDCN is characterized by a diffuse, monomorphous infiltrate of medium-sized blast cells resembling either lymphoblasts or myeloblasts. ② Nuclei have irregular contours, fine chromatin, and one to several small nucleoli. ③ The cytoplasm is usually scant and appears greyish-blue and agranular on Giemsa staining. ④ Mitoses are variable in number, and the Ki-67 proliferation index is 20-80%; angioinvasion and coagulative necrosis are absent. ⑤ In cutaneous infiltrates, the dermis is usually massively involved, with extension to the subcutaneous fat; the epidermis and adnexa are spared, with rare exceptions. ⑥ Lymph nodes are diffusely involved in the interfollicular areas and medulla, whereas B cell follicles are often spared. ⑦ Bone marrow biopsy shows either a mild interstitial infiltrate (detectable only by immunophenotyping) or massive replacement; residual haematopoietic tissue may exhibit dysplastic features, especially in megakaryocytes. ⑧ On peripheral blood and bone marrow smears, tumour cells may show cytoplasmic microvacuoles localized along the cell membrane and pseudopodia; granules and crystals are absent. | 【显微镜观察】 ① BPDCN特征性由单一中等大小的类似淋巴母细胞或髓母细胞的母细胞弥漫性浸润。 ② 细胞核轮廓不规则,染色质细腻,有一至数个小核仁。 ③ 细胞质通常很少,在姬姆萨染色中呈灰蓝色和颗粒状。 ④ 核分裂象多少不等,Ki-67增殖指数为20~80%;没有血管侵犯和凝固性坏死。 ⑤ 在皮肤浸润中,真皮通常大范围受累,并延伸至皮下脂肪;除了极少数的例外,表皮和附属器都幸免于难。 ⑥ 淋巴结滤泡间和髓质广泛受累,但含B细胞的滤泡被保留。 ⑦ 骨髓活检显示轻度间质浸润(只能通过免疫表型检测)或大范围受累;残留的造血组织可能表现出发育异常的特征,特别是在巨核细胞中。 ⑧ 在外周血和骨髓涂片上,肿瘤细胞可显示沿细胞膜和伪足定位的细胞质微泡;没有颗粒和晶体。 |
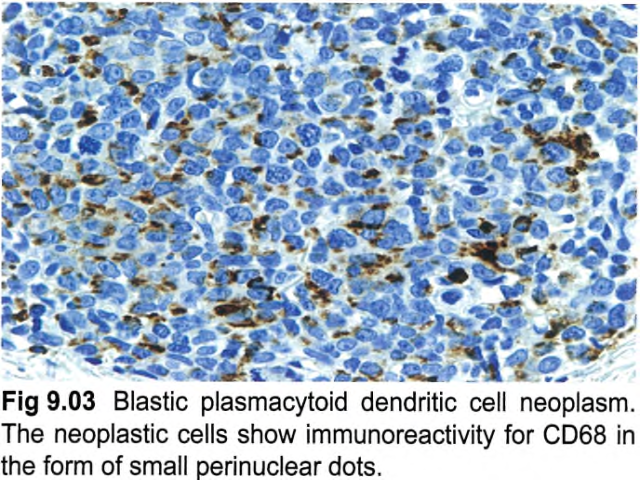
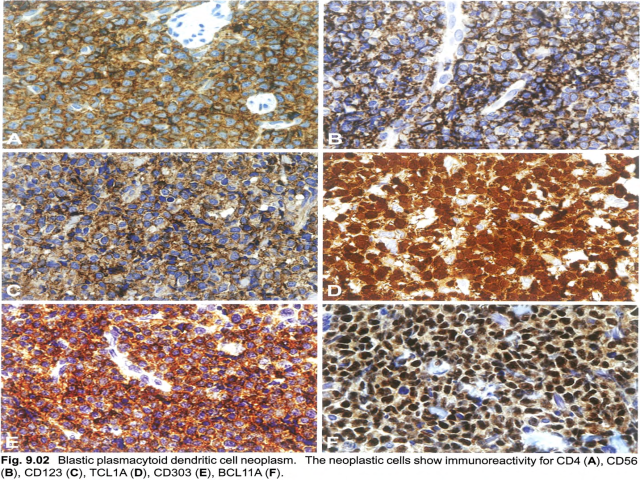
【Immunophenotype】 ① The tumour cells express CD4, CD43, CD45RA, and CD56, as well as the PDC-associated antigens CD123 (IL3 alpha-chain receptor), CD303, TCL1A, CD2AP, and SPIB and the type I interferon-dependent molecule MX1. ② Recently, the TCF4 (E2-2) transcription factor, which is essential to drive PDCs development, was found to represent a faithful diagnostic marker for BPDCN. ③ In about 8% of cases, CD4 or CD56 is negative, which does not rule out the diagnosis if other PDC-associated antigens (in particular CD123, TCL1A, or CD303) are expressed. Tumours that have some immunophenotypic features of BPDCN may be better classified as one of the subtypes of acute leukaemia of ambiguous lineage. ④ CD68 (an antigen typically expressed strongly on normal PDCs) is detected in 50-80% of cases, in the form of small cytoplasmic dots. Of the lymphoid and myeloid-associated antigens, CD7 and CD33 are relatively commonly expressed; some cases show expression of CD2, CD5, CD36, CD38, and CD79a, whereas CD3, CD13, CD16, CD19, CD20, LAT, lysozyme, and MPO are negative. ⑤ Granzyme B, which is found in normal PDCs, has also been demonstrated on flow cytometry immunophenotyping and mRNA analysis in BPDCN, but it is typically negative on tissue sections, as are other cytotoxic molecules such as perforin and TIA1. ⑥ In addition to CD56, BPDCN may also express other antigens that are usually negative in normal PDCs, such as BCL6, IRF4, and BCL2 (with BCL2 potentially acting against tumour cell apoptosis. In addition, S100 protein is expressed in 25-30% of all cases, and even more frequently in paediatric cases。 ⑦ TdT is positive in about one third of cases, with expression in 10-80% of the cells. Occasional cases express KIT (CD117). CD34 is negative on sections, but has been found by flow immunophenotyping in 17% of cases, all invariably associated with other-lineage CD34+ blasts. EBV antigens and EBV-encoded small RNA (EBER) are negative. | 【免疫表型】 ① 肿瘤细胞表达CD4、CD43、CD45RA和CD56,以及PDC相关抗原CD123(IL3α链受体)、CD303、TCL1A、CD2AP和SPIB以及I型干扰素依赖性分子MX1。 ② 最近发现,TCF4 (E2-2)转录因子是BPDCN的一个可靠的诊断标记,它是驱动PDCs发展的关键因子。 ③ 约8%的病例CD4或CD56为阴性,如其他PDC相关抗原(特别是CD123、TCL1A或CD303)表达,不排除该疾病的诊断。具有BPDCN某些免疫表型特征的肿瘤可以更好地归类为双表型急性白血病的亚型之一。 ④ CD68(一种典型的在正常PDCs强表达的抗原)在50~80%的病例中呈胞质小逗点状表达。在淋巴和骨髓相关抗原中,CD7和CD33表达相对常见;一些病例表达CD2、CD5、CD36、CD38和CD79a,而CD3、CD13、CD16、CD19、CD20、LAT、溶菌酶和MPO为阴性。 ⑤ 粒酶B在正常PDC中表达,也在流式细胞免疫分型和BPDCN 的mRNA分析中得到证实,但它在组织切片上为阴性,其他细胞毒性分子如穿孔素和TIA1也是如此。 ⑥ 除CD56外,BPDCN还可能表达其他在正常PDC中通常为阴性的抗原,如BCL6、IRF4和BCL2(BCL2可能抑制肿瘤细胞凋亡)。此外,S100在25~30%的病例中表达,在儿童病例中表达更常见。 ⑦ 约1/3病例表达TdT,10~80%的细胞阳性。偶尔表达KIT (CD117)。CD34在切片上呈阴性,但在17%的病例可通过流式检测到,所有病例都与其他谱系CD34+细胞相关。EBV抗原和EBV编码的小RNA(EBER)为阴性。 |
我要评论






共0条评论