我的博文
肠系膜病理学的诊断与难点
Key points | 关键点 |
Diagnosis of mesenteric vascular diseases can be challenging. Pathologic examination of a resection specimen sometimes is required. | 肠系膜血管疾病的诊断具有挑战性。有时需要对切除标本进行病理检查。 |
Mesenteric inflammatory disease can mimic a neoplastic process. Care must be taken in interpreting the pathologic findings. | 肠系膜炎症性疾病可以模拟肿瘤过程。在解释病理结果时必须小心。 |
Mesenteric neoplasms can be difficult to diagnose. Their diagnosis is based on familiarity with their existence and their clinical, radiologic, and histologic features. | 肠系膜肿瘤可能很难诊断。他们的诊断是基于熟悉它们的存在和其临床,影像学和组织学特征的熟悉程度。 |
Secondary involvement of the mesentery/omentum, including lymphomatosis, carcinomatosis, and sarcomatosis, always should be excluded. | 肠系膜/网膜的继发性受累应排除在外,包括淋巴瘤、癌和肉瘤。 |
EXTRAGASTROINTESTINAL STROMAL TUMOR | 胃肠外间质瘤(GIST) |
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) arise from interstitial cells of Cajal or their precursor and are among the most common mesenchymal tumors of the gastrointestinal tract. Stomach is the most common location, followed by jejunum, ileum, duodenum, and colorectum. | 胃肠道间质瘤(GISTs)起源于Cajal间质细胞或其前体,是胃肠道最常见的间质肿瘤之一。胃是最常见的部位,其次是空肠、回肠、十二指肠和结直肠。 |
A small percentage of GISTs are not connected to the gastrointestinal tract and involve omentum, mesentery, retroperitoneum, and pelvic cavity (extragastrointestinal stromal tumors [EGISTs]). | 少数GISTs不与胃肠道相连,累及网膜、肠系膜、腹膜后和盆腔(胃肠外间质瘤[EGISTs])。 |
GISTs usually spread through liver metastasis and tumor nodules in the peritoneal cavity. Lymph node metastasis is uncommon (except for the succinate dehydrogenase [SDH]-deficient type). | GISTs通常通过肝转移和腹腔肿瘤结节扩散。淋巴结转移不常见(除了琥珀酸脱氢酶缺乏型)。 |
Gross Features | 大体特征 |
Grossly, GISTS and EGISTS often are well-circumscribed masses with solid, fleshy, tan cut surfaces. Areas of hemorrhage and degeneration may be present. | 大体上,GISTS和EGISTS通常都是境界清楚的实性肿块,切面鱼肉样,棕褐色。可存在出血和变性区。 |
Microscopic Features | 镜下特征 |
GISTs can have a predominantly epithelioid or spindle cell morphology. Approximately 10% show a combination of both patterns (Fig. 17). | GISTs可以有一个以上皮样或梭形细胞为主的形态。大约有10%显示了两种模式的组合(图17)。 |
The epithelioid morphology has a nested, sheetlike architecture composed of relatively uniform cells with minimal atypia. | 上皮样形态由相对一致的细胞组成,呈巢状、片状结构,异型性小。 |
The spindle cell morphology is composed of uniform spindle cells arranged in fascicles. | 梭形细胞形态由一致的梭形细胞呈束状排列组成。 |
GISTs can be variably cellular with hyalinized stroma, hyalinized vessels, and calcification. | GISTs可细胞密度不一伴玻璃样变间质、玻璃样变血管和钙化。 |
Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis | 诊断与鉴别诊断 |
A panel of immunostains is helpful in diagnosing GISTs and distinguishing them from histologic mimics, such as leiomyoma and schwannoma. | 一组免疫染色有助于诊断GISTs,并将其与组织学相似肿瘤(如平滑肌瘤和神经鞘瘤)区分开来。 |
GISTs show diffuse and strong expression of KIT (CD117). DOG1 is a sensitive and specific immunomarker, which is positive in a majority of GISTs, including the ones that are negative for KIT. | GISTs显示弥漫性强表达KIT(CD117)。DOG1是一种敏感而特异的免疫标记物,在大多数GISTs中呈阳性,包括KIT阴性病例。 |
CD34 also is positive in 70% of GISTs. | 70%的GISTs阳性表达CD34。 |
GISTs frequently are tested for mutations of multiple genes at the same time by sequencing. | GISTs经常通过测序同时检测多个基因的突变。 |
The testing panel includes KIT, PDGFRA, BRAF, RAS, SDHA, SDHB, SDHC, SDHD, and NF1. KIT and PDGFRA mutations have treatment implications. | 检测包括KIT、PDGFRA、BRAF、RAS、SDHA、SDHB、SDHC、SDHD和NF1。KIT和PDGFRA突变具有治疗意义。 |
The Food and Drug Administration has approved small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors, namely imatinib mesylate (Gleevec, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, Basel, Switzerland) and sunitinib malate (Sutent, Pfizer Pharmaceuticals, New York, New York) for treatment of GISTs. | 美国食品和药物管理局已批准小分子酪氨酸激酶抑制剂,即甲磺酸伊马替尼(瑞士巴塞尔诺华制药公司Gleevec)和苹果酸舒尼替尼(Sunten,辉瑞制药,纽约,纽约)用于治疗GIST。 |
In contrast to carcinoma, schwannoma, and smooth muscle tumors, GISTs do not exhibit diffuse expression of S100, SOX10, or desmin; focal expression of these markers can be seen (Table 1). | 与癌、神经鞘瘤和平滑肌肿瘤相比,GIST不表现出S100、SOX10或结蛋白的弥漫性表达;可以看到这些标记物的局灶表达(表1)。 |
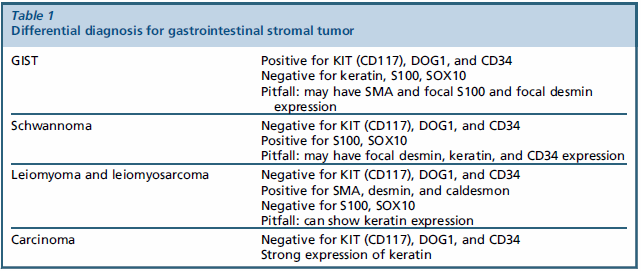
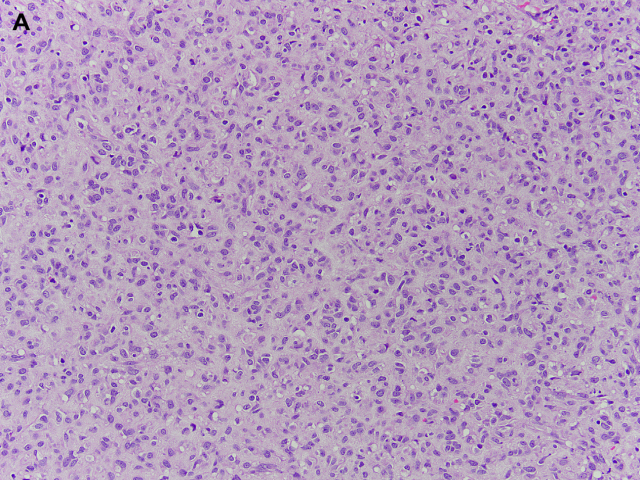
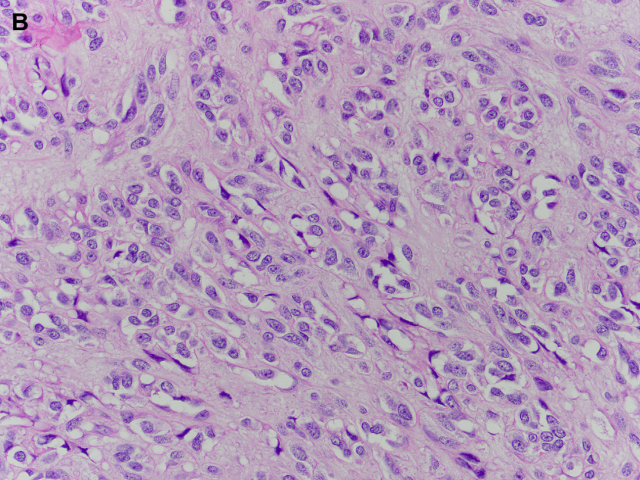
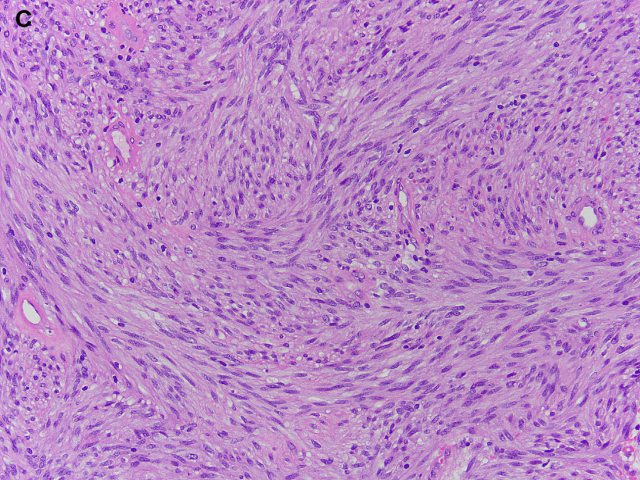
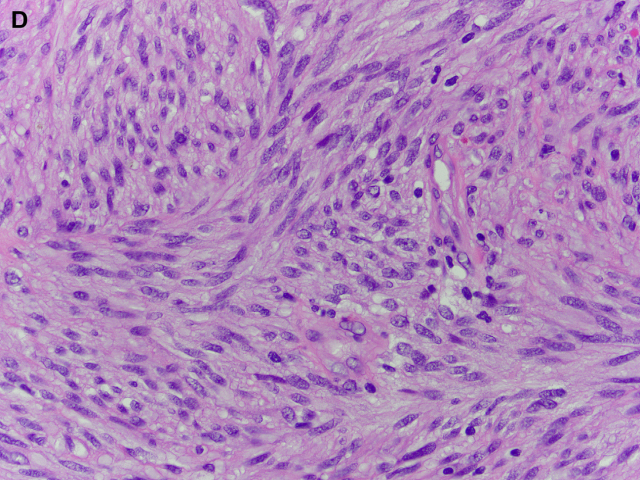
Fig. 17. GISTs. GISTs can have a predominantly epithelioid ([A] and [B]) or spindle cell morphology ([C] and [D]). Approximately 10% show a combination of epithelioid and spindle cell morphology.
我要评论






共0条评论