我的博文
to do
To map the terms of my old textbook to Ackerman. When I wanna check the mucous breast cancer in Ackerman,I've found that was difficult. It seems there is no simple equivalent in Ackerman.
So, sort out the lines of thoughts of Ackerman.
pp1659-1701
Mucinous carcinoma.#epithelium include adeno and covering# Mucinous carcinoma, also known as mucoid, colloid, or gelatinous arcinoma, usually occurs in postmenopausal women. #not influenced by estrogen?# 737,751 Grossly, it is well circumscribed, crepitant ['krepitənt] to palpation, and formed by a currant jelly-like mass held together by delicate septa (Fig.20.73). Foci of hemorrhage are frequent.
Microscopically, the classic and often quoted description is that of small clusters of tumor cells ‘floating in a sea of mucin’ (Fig. 20.74). These clusters may be solid, exhibit acinar formations, or form micropapillary structures.733 The mucin is almost entirely extracellular, and it may be of acid or neutral type.#classify the mucin type: basic,neutral, or acidic # 763 Occasionally,mucinous carcinoma will consist almost entirely of mucin, and a thorough sampling will be necessary to detect the neoplastic epithelium.757 An easily recognizable in situ component is usually absent or inconspicuous (but see later section). Histochemically, the mucins secreted by this tumor are distinct O-acylated forms of sialomucins.759 #sialo silavery sialo-adenitis? Lewis ?# Immunohistochemically, there is strong MUC2 cytoplasmic immunoreactivity and decreased MUC1 immunoreactivity compared with ductal carcinoma NOS.750,752 Both pure and mixed mucinous carcinomas of the breast often express WT1, a potentially diagnostic trap.741 Hormone receptors are always positive,#not influenced by estrogen?# while c-erbB-2 #
-erbB-2基因又称为neu或HER-2基因,是一种细胞癌基因,在多种肿瘤中其癌基因及其蛋白产物(P185)均有过度表达和扩增。对c- erbB-2癌基因蛋白产物P185的病理研究首先多见于乳腺癌,其作用也较为明确。目前普遍认为,c-erbB-2蛋白产物的阳性表达可作为判断乳腺癌预后的一个独立指标。
# is almost always negative.#contradict?# 748

# the same description " Clusters of tumor cells are seen floating in a sea of mucin" is also use to depict the similar phenomenon in gastric cancer.#
Interestingly, about a fourth to nearly half of mucinous carcinomas show features consistent with endocrine differentiation,# what is the relationship between a mucous secretion cell and endocrine cells? transdifferentiation happens here? # such as argyrophilia (Fig. 20.75), neuron-specifc enolase (NSE) immunoreactivity, and the presence of dense-core secretory granules by ultrastructural examination.734,743,745,755 This unexpected finding has raised the possibility of a link between mucinous carcinoma and the breast neoplasm originally described as carcinoid tumor (see p.1703).743,764 Some authors have suggested the existence of two types of mucinous carcinoma on the basis of the absence or presence of endocrine differentiation, which they have designated as A and B, respectively.734 Others have found that the variability of morphologic and ultrastructural features within these tumors precludes a sharp segregation,738,742 or that such segregation has no influence on survival.760 A recent gene expression profling study shows that type B mucinous carcinomas and neuroendocrine carcinomas are part of a spectrum of lesions, whereas type A mucinous carcinoma is a discrete entity.764 #underlying mechanism? any hypothesis?#
On analysis of the immunohistochemical and array-based comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) profile, pure mucinous carcinomas are homogeneous and cluster together, separately from invasive ductal carcinoma NOS.748 They less frequently harbor gains of 1q and 16p and losses of 16q and 22q than grade- and ER-matched invasive ductal carcinomas NOS.
It is important for prognostic reasons, and perhaps useful histogenetically, to restrict the term mucinous carcinoma to breast neoplasms exhibiting this feature throughout (‘pure’ mucinous carcinomas) and to exclude: (1) the ‘impure’ or ‘mixed’ tumors in which the mucinous pattern is admixed with an ordinary invasive ductal carcinoma753,761 (these having a prognosis analogous to the latter, although interestingly the molecular profile of these ‘mixed’tumors shows more similarities to pure mucinous carcinomas than invasive ductal carcinomas NOS);748 and (2) signet ring carcinomas (see p. 1709), even if technically speaking these are also ‘mucinous’tumors. Along these lines, it should be pointed out that some degree
of mucin production can be identifed in over 60% of breast carcinomas. The distinctiveness of signet ring carcinoma resides in the fact that nearly all of it remains within the cell (possibly because of a blockage in secretion), and the uniqueness of mucinous carcinoma is that most of it is extracellular (see later section). In contrast to large bowel and other sites, a combination of these two patterns is very rare in the breast.
Pure mucinous carcinoma is associated with a very low incidence (2–4%) of nodal metastases.740,751,754 The higher incidence reported in other series is probably attributable to the inclusion of ‘mixed’mucinous tumors. Consequently, the pure form of mucinous carcinoma carries an excellent short-term prognosis, particularly when the tumor measures less than 3 cm (or even less than 5 cm) in diameter.737,751 However, it has been shown that deaths from this
tumor can occur 12 years or more after therapy, indicating the need for long-term follow-up.737,758 As already indicated, several groups found no prognostic difference between the mucinous carcinomas with endocrine-like features and those without,755 although others
claim that the former are associated with favorable histologic and immunohistochemical parameters.762
Pure mucinous carcinoma is generally regarded as an invasive type of tumor. We would like to offer an alternative point of view, i.e., that this neoplasm is partially – and sometimes entirely – a form of in situ ductal carcinoma in which some component of
the mucin secretion detaches the epithelium from the underlying stroma, breaks it up in strips and nests, and engulfs it (Fig. 20.76).
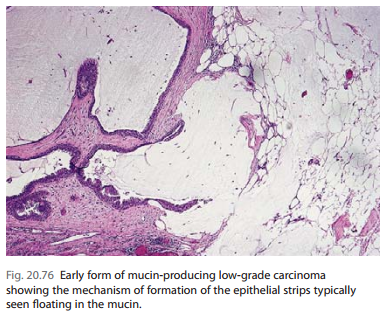
This process may be facilitated by an ‘inversion of polarity’ of the mucin secretion toward the base of the cell rather than the luminal border, as shown ultrastructurally, which is actually part of a field change.732,752 The implication is that it is the mucin, rather than the
tumor cells, that is ‘invading’ the stroma, in a fashion analogous to that often seen in mucinous tumors of the appendix.# mucus is too much, tumor cells are hustled to sea of mucus in stroma# This would explain not only the excellent prognosis of pure mucinous carcinoma but also the seemingly paradoxic fact that nearly all the mucin produced by this tumor is extracellular. Along these lines, it should be pointed out that not all mucin-containing breast nodules represent carcinomas.736 Papillomas, papillary carcinomas, and ductal hyperplasia of either the florid or atypical type can also be accompanied by focal or sometimes abundant mucin secretion,which may accumulate in large extracellular pools.747,756 Some of
these lesions have been referred to as ‘mucocele-like tumors’,757 but we feel that the term should be used in a descriptive rather than diagnostic sense. As in the appendix and other sites, the formation of a ‘mucocele’ is nearly always the expression of mucin hyperproduction and extravasation by a proliferative epithelial process,which may be hyperplastic or neoplastic, benign or malignant,in situ or invasive.744 The key determination is the nature of that process, rather than the spectacular, but relatively inconsequential, presence of the ‘mucocele’. In practical terms, a thorough sampling is always mandatory.756 Also, the fnding of mucocele-like changes in a core biopsy is an indication for surgical excision, particularly if there is epithelial atypia and/or an associated mass radiographically.735
A further variation on the theme is represented by mucinous cystadenocarcinoma, an xceptionally rare tumor composed predominantly of tall columnar cells with abundant intracytoplasmic mucin
and a multicystic gross quality similar to that of its ovarian counterpart.
Where do these mucous cells come from?
我要评论


共0条评论